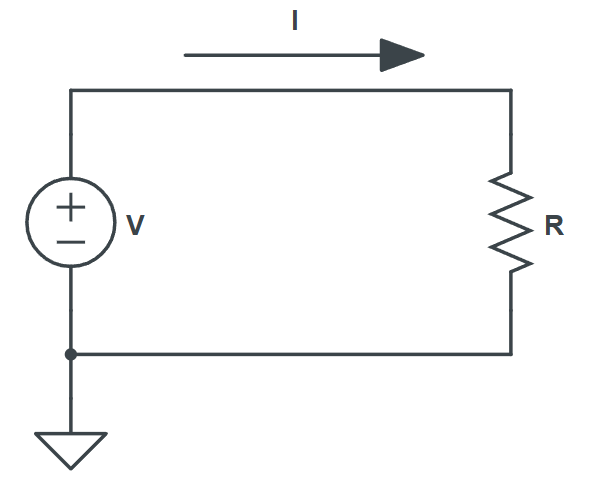
Voltage (V):
Current (I):
Resistance (R):
Using the Ohm’s Law Calculator
To effectively use the Ohm’s Law calculator, select which value you would like to calculate using the “Value to calculate” dropdown. This reveals 3 options:
- Voltage (V)
- Resistor (R)
- Current (I)
For the value you want calculated simply leave that box blank. Then, enter the two other known values. Finally, click “Calculate.” The answer will appear in the appropriate box.
For example, if I want to calculate the voltage then I would enter the known resistance and current values into the Resistance (R) and Current (I) fields, respectively. Clicking “Calculate” yields the result in the Voltage (V) field.
Calculating Voltage Using Ohm’s Law
For calculating the voltage, use the standard equation for Ohm’s Law: V = IR. That is, take the resistance R and multiply it by the current (I) flowing through that resistance.
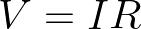
Calculating Resistance Using Ohm’s Law
The required resistance for R can be calculated using the following equation, derived from the standard Ohm’s Law equation above. Simply divide the voltage (V) by the current (I).
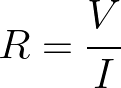
Calculating Current Using Ohm’s Law
The current (I) is calculated using the following equation. Again, this was derived from the original Ohm’s Law equation above. Simply divide the voltage (V) by the resistance (R) in the circuit. This yields the amount of current being drawn from the voltage source.
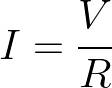
Rules for Resistor Values
The tool only allows an integer or decimal value into the resistance fields. It doesn’t understand characters like ‘k’ or ‘M’, so use the drop-down box on the side of each input box to convert the value to kilo ohms or mega ohms.
Rules for Voltage and Current Values
The tool treats voltage and current values the same way it does resistor values. Simply type in the value and select the appropriate unit from the dropdown.
Ohm’s Law FAQs
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It states that voltage (V) is equal to the product of current (I) and resistance (R), expressed as V=IR.
Ohm’s Law was discovered by German physicist Georg Simon Ohm in 1827 through a series of experiments on electric currents.
Voltage is measured in volts (V), current in amperes (A), and resistance in ohms (Ω).
Yes, Ohm’s Law can be applied to both DC and AC circuits. However, for AC circuits with reactive components like inductors or capacitors, complex math involving phase shifts may be required.
Ohm’s Law is used in designing and analyzing electrical circuits, determining resistor values, calculating power consumption, and troubleshooting electrical systems.
Meet the Author:

Hi, I’m Dominic. By day, I’m an engineer. By night, I repair and modify guitar effects! Since 2017, I’ve been independently modifying and repairing guitar effects and audio equipment under Mimmotronics Effects in Western New York. After coming out with a series of guitar effects development boards, I decided the next step is to support that community through content on what I’ve learned through the years. Writing about electronics gives me great joy, particularly because I love seeing what others do with the knowledge they gain about guitar effects and audio circuits. Feel free to reach out using the contact form!
